
The authors have designated this AOP as all rights reserved. Re-use in any form requires advanced permission from the authors.
AOP: 610
Title
A descriptive phrase which references both the Molecular Initiating Event and Adverse Outcome.It should take the form “MIE leading to AO”. For example, “Aromatase inhibition leading to reproductive dysfunction” where Aromatase inhibition is the MIE and reproductive dysfunction the AO. In cases where the MIE is unknown or undefined, the earliest known KE in the chain (i.e., furthest upstream) should be used in lieu of the MIE and it should be made clear that the stated event is a KE and not the MIE.
More help
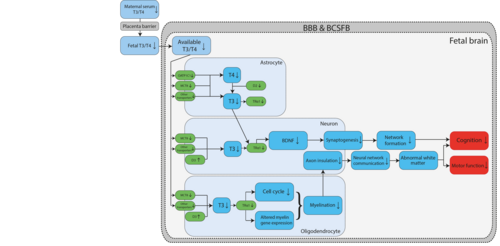
Decreased thyroid hormone levels in the brain regulated via transport, metabolism and TR activation leading to decreased cognition and motor function
Short name
A name that succinctly summarises the information from the title. This name should not exceed 90 characters.
More help
Decreased TH levels leading to developmental neurotoxicity
The current version of the Developer's Handbook will be automatically populated into the Handbook Version field when a new AOP page is created.Authors have the option to switch to a newer (but not older) Handbook version any time thereafter.
More help
Handbook Version v2.7
Graphical Representation
A graphical representation of the AOP.This graphic should list all KEs in sequence, including the MIE (if known) and AO, and the pair-wise relationships (links or KERs) between those KEs.
More help
Point of Contact
The user responsible for managing the AOP entry in the AOP-KB and controlling write access to the page by defining the contributors as described in the next section.
More help
Nathalie Dierichs
(email point of contact)
Contributors
Users with write access to the AOP page. Entries in this field are controlled by the Point of Contact.
More help
- Nathalie Dierichs
Coaches
This field is used to identify coaches who supported the development of the AOP.Each coach selected must be a registered author.
More help
OECD Information Table
Provides users with information concerning how actively the AOP page is being developed and whether it is part of the OECD Workplan and has been reviewed and/or endorsed. OECD Project: Assigned upon acceptance onto OECD workplan. This project ID is managed and updated (if needed) by the OECD. OECD Status: For AOPs included on the OECD workplan, ‘OECD status’ tracks the level of review/endorsement of the AOP . This designation is managed and updated by the OECD. Journal-format Article: The OECD is developing co-operation with Scientific Journals for the review and publication of AOPs, via the signature of a Memorandum of Understanding. When the scientific review of an AOP is conducted by these Journals, the journal review panel will review the content of the Wiki. In addition, the Journal may ask the AOP authors to develop a separate manuscript (i.e. Journal Format Article) using a format determined by the Journal for Journal publication. In that case, the journal review panel will be required to review both the Wiki content and the Journal Format Article. The Journal will publish the AOP reviewed through the Journal Format Article. OECD iLibrary published version: OECD iLibrary is the online library of the OECD. The version of the AOP that is published there has been endorsed by the OECD. The purpose of publication on iLibrary is to provide a stable version over time, i.e. the version which has been reviewed and revised based on the outcome of the review. AOPs are viewed as living documents and may continue to evolve on the AOP-Wiki after their OECD endorsement and publication.
More help
| OECD Project # | OECD Status | Reviewer's Reports | Journal-format Article | OECD iLibrary Published Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
This AOP was last modified on October 08, 2025 08:04
Revision dates for related pages
| Page | Revision Date/Time |
|---|---|
| Inhibition, monocarboxylate transporter 8 (MCT8) | November 24, 2025 09:21 |
| Antagonism, Thyroid Receptor | January 11, 2021 10:14 |
| Cell cycle, disrupted | June 30, 2021 02:56 |
| Inhibition, organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1C1 (OATP1C1) | October 08, 2025 07:16 |
| Inhibition, Deiodinase 2 | November 19, 2025 05:16 |
| Brain thyroid hormone (T4/T3) decreased | January 19, 2023 20:08 |
| Demyelination, increased | October 01, 2024 12:57 |
| Decrease of neuronal network function | May 28, 2018 11:36 |
| Altered, white brain matter | February 21, 2023 10:50 |
| Reduced levels of BDNF | April 04, 2019 09:21 |
| Decrease of synaptogenesis | September 16, 2017 10:14 |
| Locomotor function. Impaired | June 06, 2024 12:23 |
| Impairment, Learning and memory | July 26, 2024 09:54 |
| Decrease, neural network maturation | October 08, 2025 07:30 |
| Impaired axonal insulation | October 08, 2025 07:31 |
| Decreased, myelin basic protein expression in oligodendrocytes | February 21, 2023 10:41 |
| Decreased brain T4/T3 leads to BDNF, Reduced | October 08, 2025 08:00 |
| Inhibition, monocarboxylate transporter 8 (MCT8) leads to Decreased brain T4/T3 | October 08, 2025 07:31 |
| Inhibition, OATP1C1 leads to Decreased brain T4/T3 | October 08, 2025 07:57 |
| Inhibition, Deiodinase 2 leads to Decreased brain T4/T3 | October 08, 2025 07:57 |
| Decreased brain T4/T3 leads to TR Antagnoism | October 08, 2025 07:58 |
| TR Antagnoism leads to BDNF, Reduced | October 08, 2025 07:58 |
| BDNF, Reduced leads to Synaptogenesis, Decreased | April 04, 2019 11:05 |
| Synaptogenesis, Decreased leads to neural network formation | October 08, 2025 07:59 |
| neural network formation leads to Impaired locomotor function | October 08, 2025 07:59 |
| neural network formation leads to Impairment, Learning and memory | October 08, 2025 08:00 |
| TR Antagnoism leads to Cell cycle, disrupted | October 08, 2025 08:01 |
| TR Antagnoism leads to Decreased, mbp expression in oligodendrocytes | October 08, 2025 08:01 |
| Cell cycle, disrupted leads to Demyelination, increased | October 08, 2025 08:01 |
| Decreased, mbp expression in oligodendrocytes leads to Demyelination, increased | October 08, 2025 08:01 |
| Demyelination, increased leads to Impaired axonal insulation | October 08, 2025 08:02 |
| Impaired axonal insulation leads to Neuronal network function, Decreased | October 08, 2025 08:03 |
| Neuronal network function, Decreased leads to Altered, white brain matter | October 08, 2025 08:03 |
| Altered, white brain matter leads to Impairment, Learning and memory | April 12, 2024 07:46 |
| Altered, white brain matter leads to Impaired locomotor function | October 08, 2025 08:04 |
Abstract
A concise and informative summation of the AOP under development that can stand-alone from the AOP page. The aim is to capture the highlights of the AOP and its potential scientific and regulatory relevance.
More help
AOP Development Strategy
Context
Used to provide background information for AOP reviewers and users that is considered helpful in understanding the biology underlying the AOP and the motivation for its development.The background should NOT provide an overview of the AOP, its KEs or KERs, which are captured in more detail below.
More help
Strategy
Provides a description of the approaches to the identification, screening and quality assessment of the data relevant to identification of the key events and key event relationships included in the AOP or AOP network.This information is important as a basis to support the objective/envisaged application of the AOP by the regulatory community and to facilitate the reuse of its components. Suggested content includes a rationale for and description of the scope and focus of the data search and identification strategy/ies including the nature of preliminary scoping and/or expert input, the overall literature screening strategy and more focused literature surveys to identify additional information (including e.g., key search terms, databases and time period searched, any tools used).
More help
Summary of the AOP
This section is for information that describes the overall AOP.The information described in section 1 is entered on the upper portion of an AOP page within the AOP-Wiki. This is where some background information may be provided, the structure of the AOP is described, and the KEs and KERs are listed.
More help
Events:
Molecular Initiating Events (MIE)
An MIE is a specialised KE that represents the beginning (point of interaction between a prototypical stressor and the biological system) of an AOP.
More help
Key Events (KE)
A measurable event within a specific biological level of organisation.
More help
Adverse Outcomes (AO)
An AO is a specialized KE that represents the end (an adverse outcome of regulatory significance) of an AOP.
More help
| Type | Event ID | Title | Short name |
|---|
| MIE | 2258 | Inhibition, monocarboxylate transporter 8 (MCT8) | Inhibition, monocarboxylate transporter 8 (MCT8) |
| MIE | 2376 | Inhibition, organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1C1 (OATP1C1) | Inhibition, OATP1C1 |
| MIE | 1002 | Inhibition, Deiodinase 2 | Inhibition, Deiodinase 2 |
| MIE | 1656 | Antagonism, Thyroid Receptor | TR Antagnoism |
| KE | 2093 | Brain thyroid hormone (T4/T3) decreased | Decreased brain T4/T3 |
| KE | 381 | Reduced levels of BDNF | BDNF, Reduced |
| KE | 385 | Decrease of synaptogenesis | Synaptogenesis, Decreased |
| KE | 1505 | Cell cycle, disrupted | Cell cycle, disrupted |
| KE | 2105 | Decreased, myelin basic protein expression in oligodendrocytes | Decreased, mbp expression in oligodendrocytes |
| KE | 2266 | Demyelination, increased | Demyelination, increased |
| KE | 2378 | Impaired axonal insulation | Impaired axonal insulation |
| KE | 2377 | Decrease, neural network maturation | neural network formation |
| KE | 386 | Decrease of neuronal network function | Neuronal network function, Decreased |
| KE | 2108 | Altered, white brain matter | Altered, white brain matter |
| AO | 341 | Impairment, Learning and memory | Impairment, Learning and memory |
| AO | 2231 | Locomotor function. Impaired | Impaired locomotor function |
Relationships Between Two Key Events (Including MIEs and AOs)
This table summarizes all of the KERs of the AOP and is populated in the AOP-Wiki as KERs are added to the AOP.Each table entry acts as a link to the individual KER description page.
More help
| Title | Adjacency | Evidence | Quantitative Understanding |
|---|
| Decreased brain T4/T3 leads to BDNF, Reduced | non-adjacent | Not Specified | Not Specified |
Network View
This network graphic is automatically generated based on the information provided in the MIE(s), KEs, AO(s), KERs and Weight of Evidence (WoE) summary tables. The width of the edges representing the KERs is determined by its WoE confidence level, with thicker lines representing higher degrees of confidence. This network view also shows which KEs are shared with other AOPs.
More help
Prototypical Stressors
A structured data field that can be used to identify one or more “prototypical” stressors that act through this AOP. Prototypical stressors are stressors for which responses at multiple key events have been well documented.
More help
Life Stage Applicability
The life stage for which the AOP is known to be applicable.
More help
Taxonomic Applicability
Latin or common names of a species or broader taxonomic grouping (e.g., class, order, family) can be selected.In many cases, individual species identified in these structured fields will be those for which the strongest evidence used in constructing the AOP was available.
More help
Sex Applicability
The sex for which the AOP is known to be applicable.
More help
Overall Assessment of the AOP
Addressess the relevant biological domain of applicability (i.e., in terms of taxa, sex, life stage, etc.) and Weight of Evidence (WoE) for the overall AOP as a basis to consider appropriate regulatory application (e.g., priority setting, testing strategies or risk assessment).
More help
Domain of Applicability
Addressess the relevant biological domain(s) of applicability in terms of sex, life-stage, taxa, and other aspects of biological context.
More help
Essentiality of the Key Events
The essentiality of KEs can only be assessed relative to the impact of manipulation of a given KE (e.g., experimentally blocking or exacerbating the event) on the downstream sequence of KEs defined for the AOP. Consequently, evidence supporting essentiality is assembled on the AOP page, rather than on the independent KE pages that are meant to stand-alone as modular units without reference to other KEs in the sequence. The nature of experimental evidence that is relevant to assessing essentiality relates to the impact on downstream KEs and the AO if upstream KEs are prevented or modified. This includes: Direct evidence: directly measured experimental support that blocking or preventing a KE prevents or impacts downstream KEs in the pathway in the expected fashion. Indirect evidence: evidence that modulation or attenuation in the magnitude of impact on a specific KE (increased effect or decreased effect) is associated with corresponding changes (increases or decreases) in the magnitude or frequency of one or more downstream KEs.
More help
Evidence Assessment
Addressess the biological plausibility, empirical support, and quantitative understanding from each KER in an AOP.
More help
Known Modulating Factors
Modulating factors (MFs) may alter the shape of the response-response function that describes the quantitative relationship between two KES, thus having an impact on the progression of the pathway or the severity of the AO.The evidence supporting the influence of various modulating factors is assembled within the individual KERs.
More help
| Modulating Factor (MF) | Influence or Outcome | KER(s) involved |
|---|---|---|
Quantitative Understanding
Optional field to provide quantitative weight of evidence descriptors.
More help
Considerations for Potential Applications of the AOP (optional)
Addressess potential applications of an AOP to support regulatory decision-making.This may include, for example, possible utility for test guideline development or refinement, development of integrated testing and assessment approaches, development of (Q)SARs / or chemical profilers to facilitate the grouping of chemicals for subsequent read-across, screening level hazard assessments or even risk assessment.
More help
References
List of the literature that was cited for this AOP.
More help