
This AOP is licensed under the BY-SA license. This license allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, so long as attribution is given to the creator. The license allows for commercial use. If you remix, adapt, or build upon the material, you must license the modified material under identical terms.
AOP: 320
Title
Binding of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2 receptor leading to acute respiratory distress associated mortality
Short name
Graphical Representation
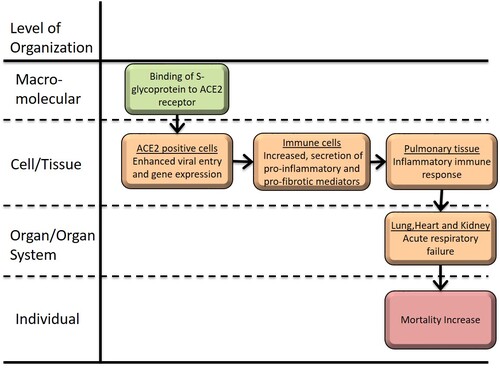
Point of Contact
Contributors
- Young Jun Kim
- Brigitte Landesmann
- Penny Nymark
- Shihori Tanabe
- Gillina Bezemer
- Julija Filipovska
- Hyunjoon Kong
- Maria Joao Amorim
- Laure-Alix Clerbaux
Coaches
- Brigitte Landesmann
- Cinzia La Rocca
OECD Information Table
| OECD Project # | OECD Status | Reviewer's Reports | Journal-format Article | OECD iLibrary Published Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.96 | Under Development |
This AOP was last modified on December 02, 2024 02:53
Revision dates for related pages
| Page | Revision Date/Time |
|---|---|
| Increased, secretion of proinflammatory mediators | May 17, 2023 15:18 |
| SARS-CoV-2 cell entry | April 04, 2023 07:39 |
| Binding to ACE2 | October 21, 2024 02:25 |
| Increase, the risk of acute respiratory failure | March 10, 2020 02:05 |
| Increased inflammatory immune responses | January 21, 2021 03:35 |
| Increased Mortality | July 08, 2022 07:32 |
| Toll Like Receptor (TLR) Dysregulation | November 23, 2021 16:54 |
| Increased SARS-CoV-2 production | June 14, 2022 08:49 |
| Interferon-I antiviral response, antagonized by SARS-CoV-2 | December 15, 2023 14:27 |
| Binding to ACE2 leads to SARS-CoV-2 cell entry | October 21, 2024 02:55 |
| SARS-CoV-2 production leads to TLR Activation/Dysregulation | April 16, 2021 04:29 |
| TLR Activation/Dysregulation leads to Increased proinflammatory mediators | February 07, 2023 23:52 |
| Increased proinflammatory mediators leads to Increased inflammatory immune responses | March 10, 2020 02:18 |
| Increased inflammatory immune responses leads to Increase, the risk of acute respiratory failure | March 10, 2020 02:19 |
| Increase, the risk of acute respiratory failure leads to Increased Mortality | May 13, 2020 09:39 |
| SARS-CoV-2 cell entry leads to IFN-I response, antagonized | December 12, 2023 15:15 |
| IFN-I response, antagonized leads to SARS-CoV-2 production | December 14, 2023 15:23 |
| SARS-CoV | March 01, 2020 10:42 |
| HCoV-NL63 | February 07, 2021 07:01 |
| Sars-CoV-2 | September 09, 2022 05:09 |
Abstract
Inhalation of substances, including viral particles, the RNA virus capsid (S) glycoprotein binds the cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and mediates fusion of the viral and cellular membranes through a pre- to postfusion conformation transition. The S protein is cleaved into S1 and S2 units by a human cell-derived protease (proteolytic enzyme) that is assumed to be Furin.S1 units then bind to its receptor, ACE2. The other fragment, S2, is cleaved by TMPRSS2, a human cell surface serine protease, resulting in cell membrane fusion. The S protein binds the catalytic domain of ACE2 with high affinities likewise, COVID-19 shares 79.6% homology of SARS-CoV and 96% identical at the whole-genome level to a bat coronavirus. The binding of the coronavirus S protein to ACE2 triggers a conformational change in the S protein of the coronavirus, allowing for proteolytic digestion by host cell proteases called TMPRSS2. The AOP reports the S glycoprotein of viral capsid in complex with its host cell receptor ACE2 resulted in acute respiratory distress associated with mortality by cytokine storms and enhanced inflammation in pulmonary tissue. S-glycoprotein of the virus uses ACE2 to get into cells that are found on the surface of epithelial cells in Kidney, Heart, Liver and Lung. However, there is an unexplored relationship for ACE2 levels between fibrotic hypersensitivity and Renin-Angiotensin Pathway which caused acute respiratory distress associated with mortality.
AOP Development Strategy
Context
The ACE2 gene encodes the angiotensin-converting enzyme-2, which has been proved to be the receptor for both the SARS-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and the human respiratory coronavirus. ACE2 is a key component of blood pressure regulation in the renin-angiotensin system. Angiotensin (Ang) converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a homolog of ACE. ACE2 negatively regulates the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) by converting Ang II to Ang-(1-7) and AngI to Ang(1-9). The higher levels of receptor expression achieved by the expression of recombinant ACE2 could be relevant for cell-cell fusion. The underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated and could play a role in the entry of the cell-free virus into cells and finally increase the acute respiratory distress associated with mortality.
Strategy
Summary of the AOP
Events:
Molecular Initiating Events (MIE)
Key Events (KE)
Adverse Outcomes (AO)
| Type | Event ID | Title | Short name |
|---|
| MIE | 1739 | Binding to ACE2 | Binding to ACE2 |
| KE | 1738 | SARS-CoV-2 cell entry | SARS-CoV-2 cell entry |
| KE | 1901 | Interferon-I antiviral response, antagonized by SARS-CoV-2 | IFN-I response, antagonized |
| KE | 1847 | Increased SARS-CoV-2 production | SARS-CoV-2 production |
| KE | 1848 | Toll Like Receptor (TLR) Dysregulation | TLR Activation/Dysregulation |
| KE | 1496 | Increased, secretion of proinflammatory mediators | Increased proinflammatory mediators |
| KE | 1750 | Increased inflammatory immune responses | Increased inflammatory immune responses |
| KE | 1748 | Increase, the risk of acute respiratory failure | Increase, the risk of acute respiratory failure |
| AO | 351 | Increased Mortality | Increased Mortality |
Relationships Between Two Key Events (Including MIEs and AOs)
| Title | Adjacency | Evidence | Quantitative Understanding |
|---|
| Binding to ACE2 leads to SARS-CoV-2 cell entry | adjacent | High | High |
| SARS-CoV-2 production leads to TLR Activation/Dysregulation | adjacent | Moderate | Not Specified |
| TLR Activation/Dysregulation leads to Increased proinflammatory mediators | adjacent | High | Not Specified |
| Increased proinflammatory mediators leads to Increased inflammatory immune responses | adjacent | High | Low |
| Increased inflammatory immune responses leads to Increase, the risk of acute respiratory failure | adjacent | Moderate | Low |
| Increase, the risk of acute respiratory failure leads to Increased Mortality | adjacent | Moderate | Not Specified |
| SARS-CoV-2 cell entry leads to IFN-I response, antagonized | adjacent | High | |
| IFN-I response, antagonized leads to SARS-CoV-2 production | adjacent | High |
Network View
Prototypical Stressors
| Name |
|---|
| SARS-CoV |
| HCoV-NL63 |
| Sars-CoV-2 |
Life Stage Applicability
| Life stage | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Conception to < Fetal | High |
Taxonomic Applicability
| Term | Scientific Term | Evidence | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Homo sapiens | Moderate | NCBI |
Sex Applicability
| Sex | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Mixed | High |
Overall Assessment of the AOP
Domain of Applicability
Essentiality of the Key Events
Evidence Assessment
Known Modulating Factors
| Modulating Factor (MF) | Influence or Outcome | KER(s) involved |
|---|---|---|
Quantitative Understanding
Considerations for Potential Applications of the AOP (optional)
This AOP not only contributes new tools to study entry of the viral particles or Inhalation of stressors into cells and localize its receptor-binding domain of ACE2 but also could serve in the development of novel vaccine immunogens against TMPRSS2 proteases which may inhibit cell entry of COVID-19.
References
- Kuba K, Imai Y, Rao S, Gao H, Guo F, Guan B, Huan Y, Yang P, Zhang Y, Deng W, Bao L, Zhang B, Liu G, Wang Z, Chappell M, Liu Y, Zheng D, Leibbrandt A, Wada T, Slutsky AS, Liu D, Qin C, Jiang C, Penninger JM (Aug 2005). "A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury". Nature Medicine. 11 (8): 875–9. doi:10.1038/nm1267. PMID 16007097.
- "What are the official names of the disease and the virus that causes it?". Q&A on coronaviruses. World Health Organization. Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- Zhou P, Yang X (2020-02-03). "A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated With a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin". Nature. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. PMID 32015507.
- Xintian, Xu; Chen, Ping (2020). "Evolution of the novel coronavirus from the ongoing Wuhan outbreak and modeling of its spike protein for risk of human transmission". Science China Life Sciences. doi:10.1007/s11427-020-1637-5. PMID 32009228.
- Understanding COVID-19 through adverse outcome pathways – 2nd CIAO AOP Design Workshop doi.org/10.14573/altex.2102221
- Lewis, Ricki. "COVID-19 Vaccine Will Close in on the Spikes". DNA Science Blog. Public Library of Science. Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- Walls, Alexandra; et al. (2020). "Structure, function and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein". bioRxiv. bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2020.02.19.956581. Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- He L,et al (2006).Expression of elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in SARS-CoV-infected ACE2+ cells in SARS patients: relation to the acute lung injury and pathogenesis of SARS.J Pathol. 2006 Nov;210(3):288-97.
- Daniel Wrapp, Nianshuang Wang, Kizzmekia S. Corbett , Jory A. Goldsmith, Ching-Lin Hsieh , Olubukola Abiona , Barney S. Graham , Jason S. McLellan Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation Wrapp et al., Science 367, 1260–1263 (2020)
- Hamming I, Timens W, Bulthuis ML, Lely AT, Navis G, van Goor H Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis J Pathol. 2004 Jun;203(2):631-7
- Xie Xudong et al.Age- and gender-related difference of ACE2 expression in rat lung Life Sciences Volume 78, Issue 19, 4 April 2006, Pages 2166-2171
- Kim Y et al. Advanced Adverse Outcome Pathways Potentially Bridging the Pathogenesis of COVID-19, 2021, doi: 10.20944/preprints202101.0065.v1
- Penny Nymark et al. Systematic Organization of COVID-19 Data Supported by the Adverse Outcome Pathway Framework, 2021,doi: 10.20944/preprints202101.0573.v1
- Mathieu Vinke, A putative AOP for pneumonia related to COVID-19, 2020, Archives of Toxicology 94(9)
- Sally A, Mayasich et al. In Silico Analysis of Cross-Species Sequence Variability in Host Interferon Antiviral Pathway Proteins and SARS-CoV-2 Susceptibility