
This AOP is licensed under the BY-SA license. This license allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, so long as attribution is given to the creator. The license allows for commercial use. If you remix, adapt, or build upon the material, you must license the modified material under identical terms.
AOP: 388
Title
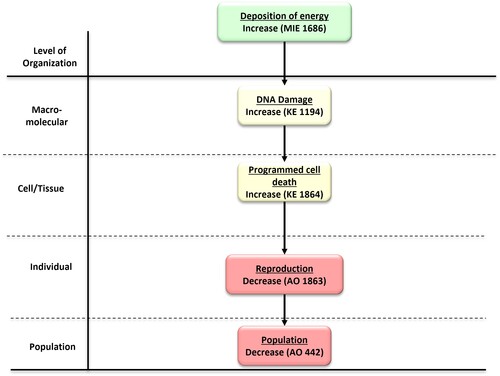
Deposition of ionising energy leading to population decline via programmed cell death
Short name
Graphical Representation
Point of Contact
Contributors
- Knut Erik Tollefsen
- You Song
- Li Xie
Coaches
OECD Information Table
| OECD Project # | OECD Status | Reviewer's Reports | Journal-format Article | OECD iLibrary Published Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
This AOP was last modified on April 29, 2023 16:03
Revision dates for related pages
| Page | Revision Date/Time |
|---|---|
| Increase, Programmed cell death | April 12, 2021 02:17 |
| Decrease, Reproduction | April 11, 2021 17:38 |
| Decrease, Population growth rate | January 03, 2023 09:09 |
| Deposition of Energy | August 23, 2024 09:20 |
| Increase, DNA damage | May 08, 2019 12:28 |
| Energy Deposition leads to Increase, DNA Damage | January 21, 2022 07:18 |
| Increase, DNA Damage leads to Increase, Programmed cell death | April 11, 2021 09:21 |
| Increase, Programmed cell death leads to Decrease, Reproduction | January 21, 2022 07:19 |
| Decrease, Reproduction leads to Decrease, Population growth rate | April 11, 2021 08:26 |
| Ionizing Radiation | May 07, 2019 12:12 |
| Ultraviolet B radiation | April 15, 2017 16:04 |
| Gamma radiation | April 15, 2017 16:04 |
Abstract
Ionising and non-ionizing radiation can induce DNA damage (strand breaks, abatic sites, oxidized bases, and DNA-proteincross-links) in cells of primary producers. Excessive DNA strand breaks can trigger programmed cell death leading to reduction in development (size and weight) and/or reproduction (number of organisms and/or leaves) to reduce the overall population.
AOP Development Strategy
Context
Strategy
Summary of the AOP
Events:
Molecular Initiating Events (MIE)
Key Events (KE)
Adverse Outcomes (AO)
| Type | Event ID | Title | Short name |
|---|
| MIE | 1686 | Deposition of Energy | Energy Deposition |
| KE | 1194 | Increase, DNA damage | Increase, DNA Damage |
| KE | 1864 | Increase, Programmed cell death | Increase, Programmed cell death |
| AO | 1863 | Decrease, Reproduction | Decrease, Reproduction |
| AO | 360 | Decrease, Population growth rate | Decrease, Population growth rate |
Relationships Between Two Key Events (Including MIEs and AOs)
| Title | Adjacency | Evidence | Quantitative Understanding |
|---|
| Energy Deposition leads to Increase, DNA Damage | adjacent | High | High |
| Increase, DNA Damage leads to Increase, Programmed cell death | adjacent | High | High |
| Increase, Programmed cell death leads to Decrease, Reproduction | adjacent | High | High |
| Decrease, Reproduction leads to Decrease, Population growth rate | adjacent | High | High |
Network View
Prototypical Stressors
Life Stage Applicability
| Life stage | Evidence |
|---|---|
| All life stages | |
| Adult, reproductively mature | High |
Taxonomic Applicability
| Term | Scientific Term | Evidence | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lemna minor | Lemna minor | High | NCBI |
Sex Applicability
| Sex | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Unspecific | High |
| Hermaphrodite | Low |
Overall Assessment of the AOP
The evidence for the MIE, KE and AO were considered Moderate to High for all Key Events and Key Event Relationships. The overall assessment of the AOP were considered Moderate.
Domain of Applicability
Taxonomic: all primary producers
Life stage: all stages
Sex: both genders (dioecious plants) and not relevant (hermaphrodites)
Stressors: Ionizing radiation, Ultraviolet B radiation (UVB)
Essentiality of the Key Events
The essentiality of all key events was considered as Moderate to High. Essentiality evaluations were mainly based on specifically designed studies demonstrating the expected effect pattern predicted by the AOP to occur after exposure to Cobalt-60 external radiation (ionising radiation) and Ultraviolet B radiation (UVB) .
Evidence Assessment
Biological Plausibility:
Empirical Evidence:
Overall confidence in the AOP:
Known Modulating Factors
Quantitative Understanding
Quantitative data were generated in studies with Lemna minor and the freshwater algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii exposed to external gamma radiation from a Cobalt-60 source (ionizing radiation) and artificial UVB (non-ionizing radiation). The quantitative understanding of the AOP was therefore considered to be Moderate for these species.
Considerations for Potential Applications of the AOP (optional)
References
Xie, L., Solhaug, K. A., Song, Y., Brede, D. A., Lind, O. C., Salbu, B., & Tollefsen, K. E. (2019). Modes of action and adverse effects of gamma radiation in an aquatic macrophyte Lemna minor. Science of the Total Environment, 680, 23-34.
Xie, L., Solhaug, K. A., Song, Y., Johnsen, B., Olsen, J. E., & Tollefsen, K. E. (2020). Effects of artificial ultraviolet B radiation on the macrophyte Lemna minor: a conceptual study for toxicity pathway characterization. Planta, 252(5), 1-18.